|
|
3 jaren geleden | |
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| data | 3 jaren geleden | |
| images | 3 jaren geleden | |
| scripts | 3 jaren geleden | |
| README.md | 3 jaren geleden | |
README.md
The project creates a star schema and insert data from data sources using Amazon Redshift. One fact table and four dimension are created as the following. This is a project on Udacity nanodegree of data engineering.
Data Sources
The log and song data files to be processed are provided by Udacity and are located in Udacity's s3 bucket. A jsonpath file for log data is also provided, and the jsonpath file for song data is also created.
Assumption
The project assumes that all records in log data files are unique and the users' information is the newer with larger timestamp. Since a song file contains only one song, the project assumes that a song record with large song number is newer. The project assumes that an instance of Amazon Redshift is already created and the file dwh.cfg should be filled out.
Scripts
The python file sql_queries.py defines all the SQL statements needed, including create table statement and insert statement. The python file create_tables.py should be executed first to create necessary tables. The etl.py will first copy data to staging tables and then insert data into the following tables.
Fact Table:
Table Name: songplays
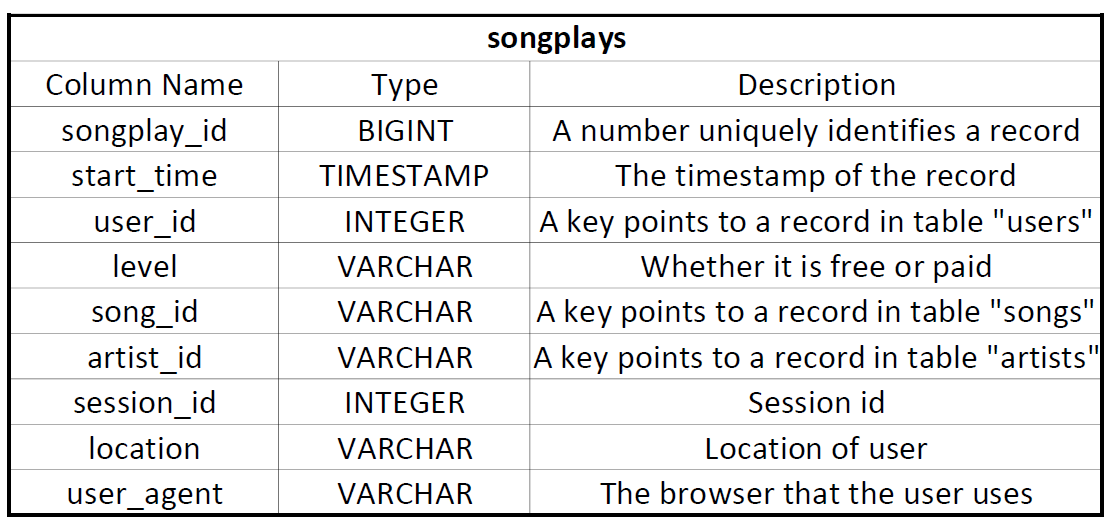 The start_time field is chosen to be the sort key and user_id field is choosen to be the distribution key.
The start_time field is chosen to be the sort key and user_id field is choosen to be the distribution key.
Dimension Tables:
Table Name: user
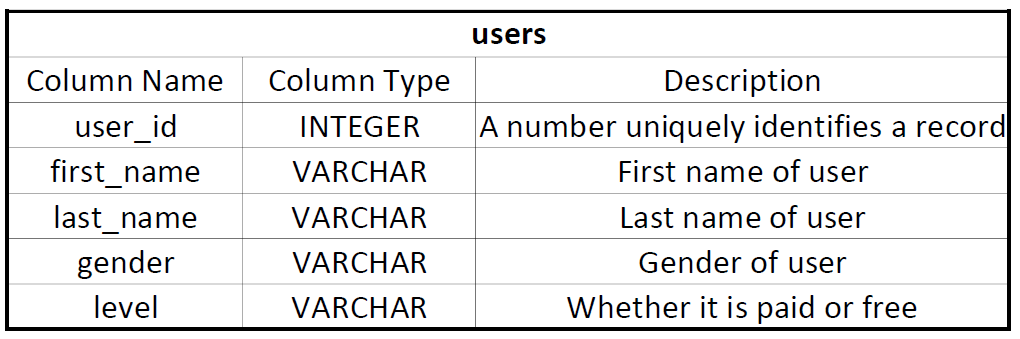 The user_id field is chosen to be the sort key and the whole table has a distribution style of "all".
The user_id field is chosen to be the sort key and the whole table has a distribution style of "all".
songs
Table Name: songs
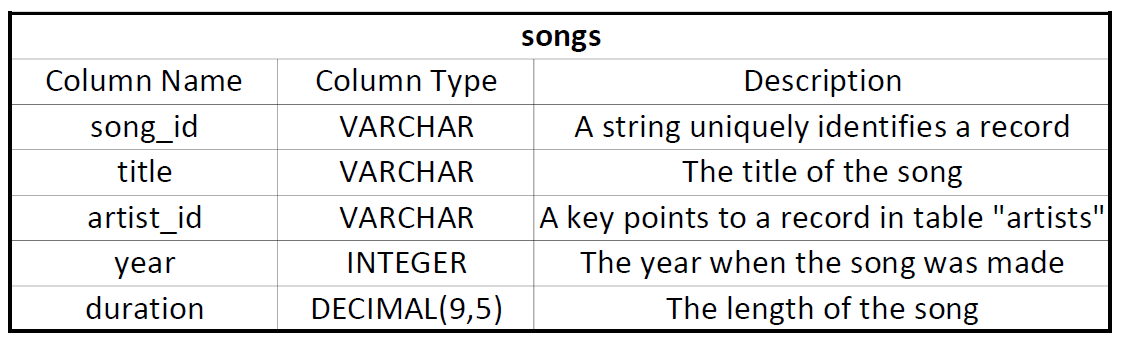 The table is sorted by song_id and distributed by artist_id.
The table is sorted by song_id and distributed by artist_id.
artists
Table Name: artists
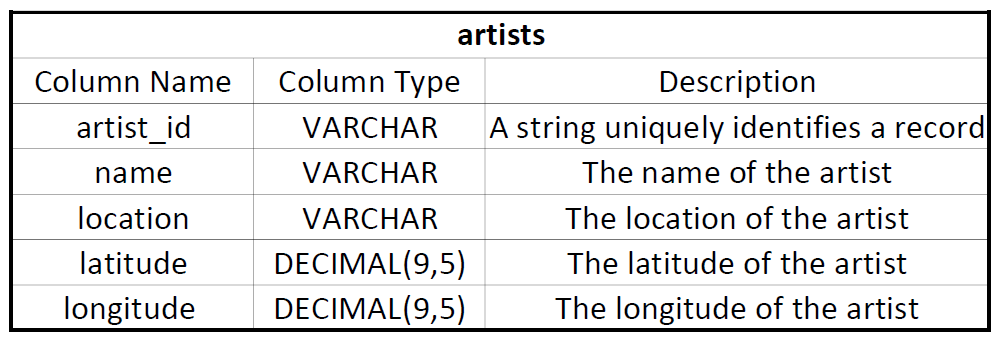 The table is sorted by artist_id and has a distribution stytle of "all".
The table is sorted by artist_id and has a distribution stytle of "all".
time
Table Name: time
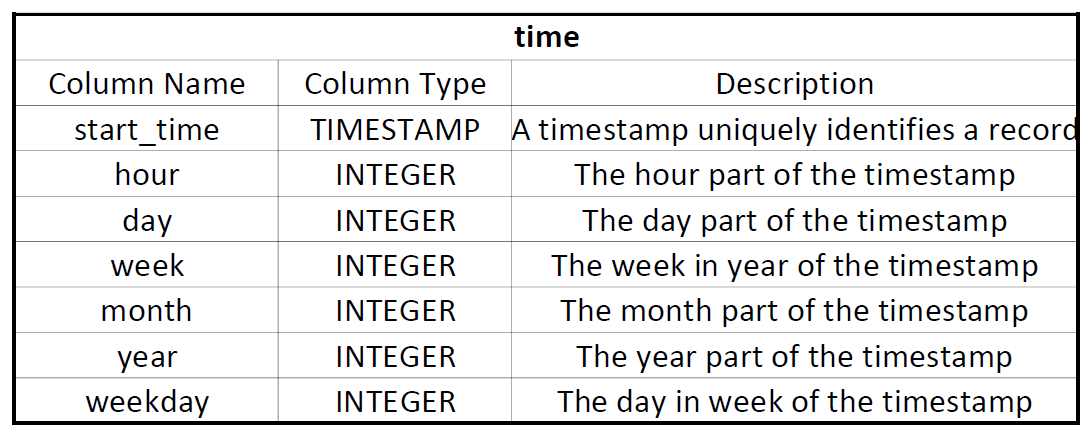 The table is sorted by start_time and has a distribution stytle of "all"
The table is sorted by start_time and has a distribution stytle of "all"
Staging Tables
Two staging tables are also created to copy data from files. All columns of the staging tables are nullable so that data can be loaded successfully. After records are copied into the staging tables, the corresponding columns are selected and inserted into fact and dimension tables. The staging tables will be kept in the cloud until they are not needed.
Examples of Database Usage
In order to find the pattern of users' activities, a data consumer can query as follow:
SELECT songplays.start_time, COUNT(songplays.start_time) AS count_tm
From songplays JOIN time
ON songplays.start_time = time.start_time
WHERE time.year = 2018
AND time.month = 10
GROUP BY songplays.start_time ORDER BY songplays.start_time;
To find the most popular artists and to retrieve their informations, a data consumer can do the following:
SELECT artists.artist_id, artists.name, count_table.count_artist FROM (
SELECT artist_id, COUNT(artist_id) AS count_artist
FROM songplays
GROUP BY artist_id
) AS count_table
JOIN artists
ON count_table.artist_id = artists.artist_id
ORDER BY count_table.count_artist DESC
LIMIT 10;